Understanding Self-Managed Networks: A Comprehensive Guide
- Phone: +1(833)PHX-Geek
- 712 H St NE Suite 1904 Washington, D.C. 20002
Are you looking to come to Toast POS? Follow this link to sign up and get a free quote from your local Toast Rep. They will come out to your restaurant, and give you a free, no obligation quote.
Introduction
A self-managed network is a telecommunications setup that allows users to control and manage their network connectivity without relying on external service providers. This model empowers organizations to configure, monitor, and maintain their network infrastructure according to their specific needs and preferences. With technological advancements and the increasing complexity of network environments, the appeal of self-managed networks has gained significant traction.
Self-managed networks typically utilize a combination of hardware and software solutions, enabling users to create a tailored networking environment. By leveraging automation and monitoring tools, businesses can ensure optimal performance while reducing dependency on third-party providers. This approach fosters agile responses to network demands and allows for real-time adjustments based on usage patterns.
Adopting a self-managed network not only streamlines operations but also enhances security. Organizations can implement custom security measures that align with their unique requirements, as opposed to relying on standardized protocols. This level of control is particularly valuable in industries with strict regulatory compliance, where data protection is paramount.
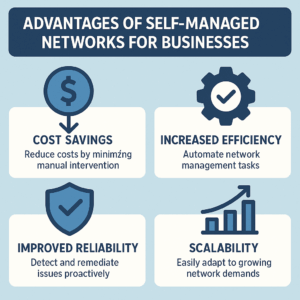
One of the primary advantages of self-managed networks is cost-effectiveness. Organizations can avoid recurring fees associated with managed services by taking control of their networking infrastructure. This financial flexibility allows for reinvestment in other critical areas, such as staff training or technology upgrades, ultimately driving growth.
Additionally, self-managed networks provide enhanced customization. Companies can tailor configurations to suit their operational needs, optimizing performance and efficiency. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for businesses that experience fluctuating demands or require unique network setups for specific projects.
Another notable benefit is the increased visibility and control over network performance. By managing their own networks, organizations can monitor traffic patterns and identify potential bottlenecks or vulnerabilities. This proactive approach enables timely interventions and fosters a culture of continuous improvement within the organization.
While self-managed networks offer numerous advantages, they also come with challenges that organizations must consider. One significant concern is the technical expertise required to effectively manage the network. Without the right skills and knowledge, companies may struggle to maintain optimal performance, leading to potential downtime and data breaches.
Moreover, the initial setup of a self-managed network can be resource-intensive. Organizations may need to invest in new hardware and software, as well as allocate time for staff training. This upfront investment can pose challenges, particularly for smaller companies with limited budgets.
 Finally, businesses must remain vigilant regarding ongoing network security. A self-managed approach places the responsibility for security measures squarely on the organization’s shoulders. Regular updates, patches, and monitoring are essential to mitigate risks and protect sensitive data from potential threats.
Finally, businesses must remain vigilant regarding ongoing network security. A self-managed approach places the responsibility for security measures squarely on the organization’s shoulders. Regular updates, patches, and monitoring are essential to mitigate risks and protect sensitive data from potential threats.
As technology continues to evolve, self-managed networks are expected to undergo significant advancements. The rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning will likely play a pivotal role in automating network management tasks, enabling organizations to optimize their networks with greater efficiency and accuracy.
Additionally, the growing emphasis on remote work will drive demand for more flexible and scalable self-managed networking solutions. Businesses will seek to create adaptive environments that can support a distributed workforce, allowing employees to connect securely from various locations.
Finally, advancements in cloud computing will further enhance the capabilities of self-managed networks. By leveraging cloud technologies, organizations can access powerful tools and resources that facilitate real-time data analysis and performance monitoring, ultimately paving the way for more informed decision-making.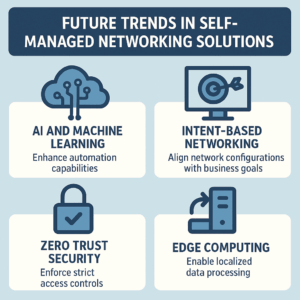
Conclusion
Self-managed networks represent a transformative approach to managing connectivity within organizations. While they offer distinct advantages, understanding the associated challenges is crucial for successful implementation. As technology continues to advance, businesses that embrace this model will be better positioned to meet the demands of a rapidly evolving digital landscape.